The term Pyrolysis is derived from two Greek words: pyro – fire and lysis – separating and is a process where carbon-based (organic) materials are chemically decomposed by applying extremely high temperatures. It is also the first step in combustion and gasification and occurs in the absence of oxygen, a distinctive factor that separates the process from normal combustion which can only take place only if oxygen is present at sufficient levels. The rate of pyrolysis reaction increases with an increase in temperature.

Pyrolysis normally occurs at temperatures exceeding 430 degrees Celsius and under pressure. It is also worth noting that the process involves the change of the matter’s chemical composition and physical phase and is irreversible. The process is often used to transform organic materials into solid residues containing carbon, ash, and small quantities of gases and liquids. Extreme pyrolysis yields carbon as the main residue and is generally referred to as carbonization.
Unlike other processes involving high temperatures such as combustion and hydrolysis, pyrolysis doesn’t involve reaction with oxygen, water, or any other reagent. However, as it’s virtually impossible to achieve oxygen-free environments, small amounts of oxidation will always occur within a pyrolysis system (planta de pirólisis).
Types of Pyrolysis Reaction
When it comes to pyrolysis application, there are basically three types of reactions differentiated by biomass temperature and the processing time. These are:
Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis is distinguished by its low temperatures, slow biomass heating rates, and lengthy gas and solids residence times. Under this option, heating temperatures range from between 32.18 to 35.6 degrees Fahrenheit with the prevailing temperatures being around 932 degrees Fahrenheit. The gas residence time may be somewhere over five seconds, while that of biomass ranging from a couple of minutes to days. Under this process, char and tar are released as the main end products due to the slow devolatilization of biomass.
Flash Pyrolysis
Flash pyrolysis is when biomass is subjected to rapid heating rates at moderate temperatures that range from 753 to 1112 degrees Fahrenheit. However, the process’ vapor residence time is less than 2 seconds. The process produces lesser amounts of tar and gas compared to the latter.
Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis is mainly used to produce gas and bio-oil. Under this process, the biomass is heated rapidly to between 1202 to 1832 degrees Fahrenheit to attain the amount of gas or bio-oil products desired. Under this process, large quantities of char are accumulated and have to be removed often.
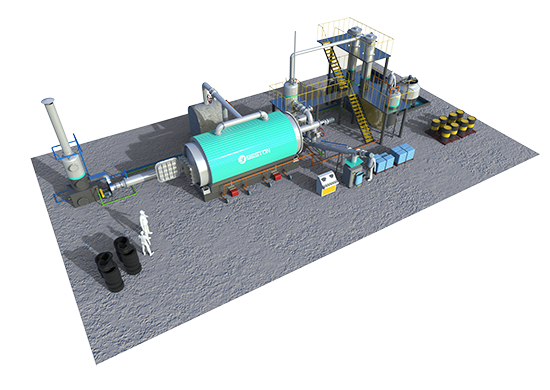
Tire pyrolysis: www.bestoneco.com/planta-pirolisis-neumaticos/
Benefits of Pyrolysis Reaction
Here is a look at some of the key benefits of the pyrolysis process
– It reduces greenhouse gas emissions and the amount of waste going to landfills
– It’s a simple, low-cost technology for the processing of a wide range of feedstocks
– It has the potential of helping countries reduce their dependence on imported energy by generating their own using domestic resources (recursos domesticos)
– Construction of pyrolysis power plants is relatively easy and fast
– It reduces water pollution risks
– Waste management using modern pyrolysis technology is way cheaper than disposing of waste in landfills
– The process plays a crucial role in mass spectrometry and carbon-14 dating
Applications
Pyrolysis is widely used in the chemical industry to produce activated carbon charcoal, methanol, and other wood substances. It is also used to produce synthetic gas that can be used to power electricity-generating steam or gas turbines. Also, the mixture of ceramics, glass, soil, and stones obtained from the pyrolysis process can be used as building materials.